ISRA FACTSHEETS
ISRA FACTSHEETS
ASIA REGION
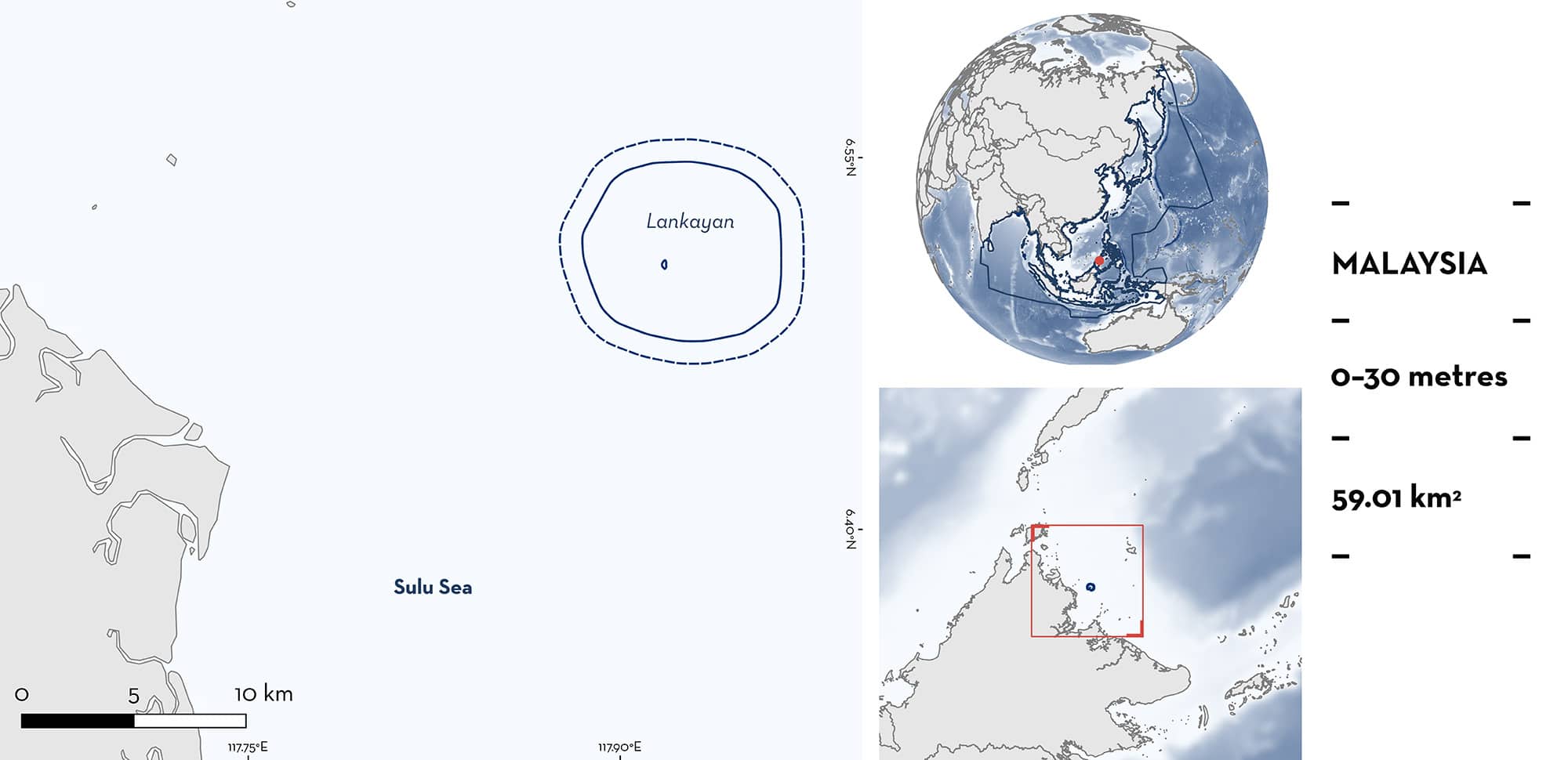
Lankayan
Summary
Lankayan is located off the northeast coast of Sabah, Malaysia. This area includes the island of Lankayan and its surrounding coral reefs. The habitat is characterised by shallow coral reef flats, reef slopes, patch reefs, seagrass beds, and sandy areas. It is influenced by the monsoon season, with wetter weather during November–March. Lankayan overlaps with the Sugud Islands Marine Conservation Area Marine Protected Area and the Sulu-Sulawesi Marine Ecoregion Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Area. Within this area there are: threatened species (e.g., Indo-Pacific Leopard Shark Stegostoma tigrinum); reproductive areas (Blacktip Reef Shark Carcharhinus melanopterus); feeding areas (Blacktip Reef Shark); and resting areas (Indo-Pacific Leopard Shark).
Download factsheet
Lankayan
DESCRIPTION OF HABITAT
Lankayan is located ~20 km off the northeast coast of Sabah, Malaysia. The area is centred around Lankayan Island, a small, low-lying coral island with enclosed fringing reef flats that extend to between 50 m to 1 km from shore (Teh et al. 2008). The reef flats are shallow at ~0.5–2 m depth, with the outer slope ranging from 5–16 m. The area also contains many small (~0.5 ha) to large (~400 ha) patch reefs. The habitat is also characterised by sandy areas and seagrass beds at the shallow inner edge of the island and in some deeper areas.
The weather pattern in Lankayan is subject to two monsoon cycles: the drier southwest monsoon (May–September) and the wetter northeast monsoon (November–March). In the waters surrounding Lankayan, a semidiurnal tide is observed, featuring two tidal cycles in a 24-hour and 50-minute period.
Lankayan Island overlaps with the Sugud Islands Marine Conservation Area (SIMCA) and with the Sulu-Sulawesi Marine Ecoregion Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Area (EBSA; CBD 2024).
This Important Shark and Ray Area is benthopelagic and is delineated from inshore and surface waters (0 m) to 30 m based on the bathymetry of the area and the depth range of the Qualifying Species in the area.
CRITERION A
VULNERABILITY
Two Qualifying Species considered threatened with extinction according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species regularly occur in the area. These are the Endangered Indo-Pacific Leopard Shark (Dudgeon et al. 2019) and the Vulnerable Blacktip Reef Shark (Simpfendorfer et al. 2020).
CRITERION C
SUB-CRITERION C1 – REPRODUCTIVE AREAS
Lankayan is an important reproductive area for one shark species.
Small Blacktip Reef Sharks are regularly seen in shallow sandy waters around Lankayan Island (A Chung & DA Spiji pers. obs. 2024). Visual estimates of 30–50 cm total length (TL) are within the range of the species’ size-at-birth (48 cm TL; Chin et al. 2013) and indicate that these are likely to be neonates and young-of-the-year (YOY). A single group of 5–8 individuals is seen each season, and they are often observed on shallow sandy substrates near the shoreline around the island. Sightings have been reported more frequently since 2015, particularly from 2020–2024. These consist of daily sightings in September and October for 1–2 months and of regular sightings almost every week, from December to May (A Chung & DA Spiji pers. obs. 2024; A Amil pers. comm. 2024). Blacktip Reef Sharks were smallest in September/October (L Sikim & A Amil pers. comm. 2024), indicating that this may be the pupping season. The shallow sandy substrate near the shoreline is a suitable habitat for them to avoid predation from larger sharks that are found in relatively deeper waters off the reef flat. Neonate/YOY individuals were also observed swimming around schools of small fishes along the shoreline, which suggests that they might be feeding on these fishes. Sightings in October–November 2023 and January 2024 indicate that the neonates are resident in a small area near the island, while as YOY later in the season, they are seen ~3 times per week, at different locations around the island and usually in the early morning (6–8 am), but they do not stay throughout the day at the same area like the neonates do (A Amil &JE Sadim pers. comm. 2024). It is possible that this change is driven by the small schooling fishes seasonally moving away from the shoreline. The area therefore provides refugia from predation and abundant food resources for neonate Blacktip Reef Sharks before they disperse to deeper waters as they grow older.
CRITERION C
SUB-CRITERION C2 – FEEDING AREAS
Lankayan is an important feeding area for one shark species.
Blacktip Reef Sharks seasonally feed on Green Turtle Chelonia mydas hatchlings in this area (JE Sadim pers. comm. 2024). Lankayan Island is a known nesting beach for Green Turtles (Teh et al. 2008), with ~500 nests recorded each year. The turtle eggs are transferred to sea turtle hatcheries by rangers and the hatchlings are immediately released into the sea. Blacktip Reef Sharks frequently feed on turtle hatchlings, especially during the peak hatching season from September–November, two months after the peak nesting season. It is estimated that these sharks prey on the turtle hatchlings about twice a week when they are released into the sea during the peak hatching season, despite measures taken by the rangers to avoid predation of these hatchlings by the sharks, such as releasing the turtle hatchlings at different beach points and during sunset and night time. Small and large individuals feed on turtle hatchlings, with an average of ~4 small and ~2 large individuals per feeding event. It appears that the Blacktip Reef Shark reproductive cycle in Lankayan matches the turtle hatching seasonality, with neonates born at the start of the peak turtle hatching season, providing a reliable food source for these pups. Blacktip Reef Sharks are known to seasonally feed on turtle hatchlings elsewhere (Bashir et al. 2020), and it is likely that Lankayan is also an important seasonal feeding ground for the species. Additionally, neonate and YOY Blacktip Reef Sharks have been regularly observed around schools of small fishes on the island’s shoreline, which could be a potential prey source for them (A Chung & DA Spiji pers. obs. 2024).
CRITERION C
SUB-CRITERION C3 – RESTING AREAS
Lankayan is an important resting area for one shark species.
Indo-Pacific Leopard Sharks are regularly sighted resting on the sandy substrate around a shipwreck dive site that has two sunken wrecks separated by ~70 m (A Chung, DA Spiji & L Sikim pers. obs. 2024). Groups of up to five individuals have been seen resting together at any one time since 2009, although since 2018, single individuals have been more frequently seen than groups. Sightings are common, with a 50% frequency per dive at this site, and about three dives conducted here per week since 2019, and individuals are almost always seen resting. The species is also seen swimming and resting at other sites around Lankayan, but they are more regularly seen resting at the shipwreck site than other sites around the area (N Tamil pers. comm. 2024).
Download factsheet
SUBMIT A REQUEST
ISRA SPATIAL LAYER REQUEST
To make a request to download the ISRA Layer in either a GIS compatible Shapefile (.shp) or Google Earth compatible Keyhole Markup Language Zipped file (.kmz) please complete the following form. We will review your request and send the download details to you. We will endeavor to send you the requested files as soon as we can. However, please note that this is not an automated process, and before requests are responded to, they undergo internal review and authorization. As such, requests normally take 5–10 working days to process.
Should you have questions about the data or process, please do not hesitate to contact us.